A year ago, Pluto was just a bright speck in the cameras of NASA’s approaching New Horizons spacecraft, not much different than its appearances in telescopes since Clyde Tombaugh discovered the then-ninth planet in 1930.
But this week, in the journal Science, New Horizons scientists have authored the first comprehensive set of papers describing results from last summer’s Pluto system flyby. “These five detailed papers completely transform our view of Pluto – revealing the former ‘astronomer’s planet’ to be a real world with diverse and active geology, exotic surface chemistry, a complex atmosphere, puzzling interaction with the sun and an intriguing system of small moons,” said Alan Stern, New Horizons principal investigator from the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, Colorado.
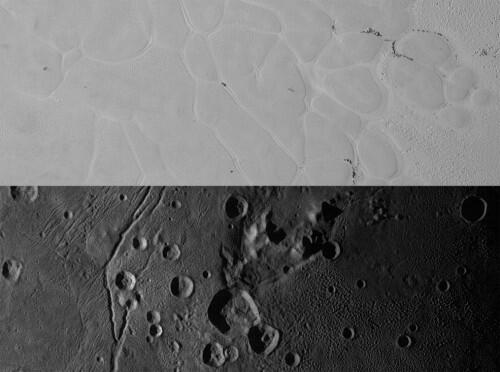
Above are New Horizons’ views of the informally named Sputnik Planum on Pluto (top) and the informally named Vulcan Planum on Charon (bottom). The Sputnik Planum strip measures 228 miles (367 kilometers) long, and the Vulcan Planum strip measures 194 miles (312 kilometers) long. Illumination is from the left. The bright, nitrogen-ice plains are defined by a network of crisscrossing troughs. This observation was obtained by the Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) at a resolution of 1,050 feet (320 meters) per pixel. The Vulcan Planum view in the bottom panel includes the “moated mountain” Clarke Mons just above the center of the image. The water ice-rich plains display a range of surface textures, from smooth and grooved at left, to pitted and hummocky at right. This observation was obtained by the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) at a resolution of 525 feet (160 meters) per pixel. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI
After a 9.5-year, 3-billion-mile journey – launching faster and traveling farther than any spacecraft to reach its primary target – New Horizons zipped by Pluto on July 14, 2015. New Horizons’ seven science instruments collected about 50 gigabits of data on the spacecraft’s digital recorders, most of it coming over nine busy days surrounding the encounter.
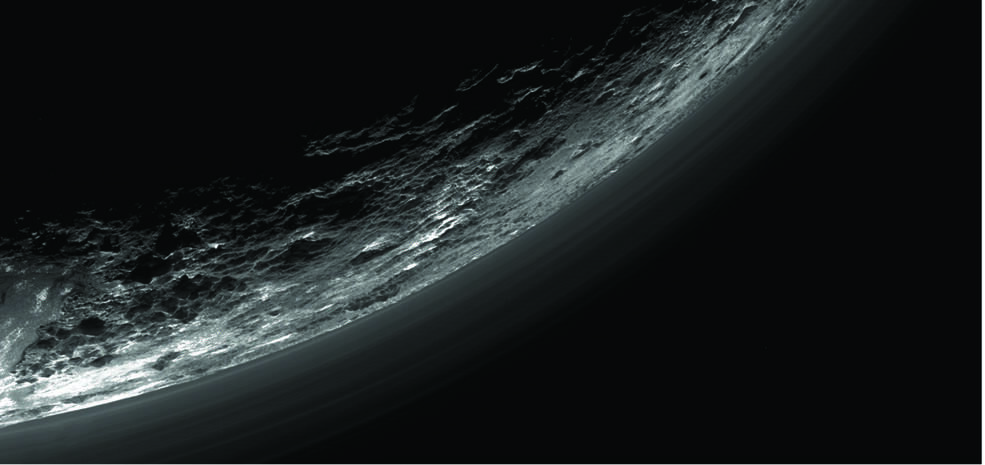
The first close-up pictures revealed a large heart-shaped feature carved into Pluto’s surface, telling scientists that this “new” type of planetary world – the largest, brightest and first-explored in the mysterious, distant “third zone” of our solar system known as the Kuiper Belt – would be even more interesting and puzzling than models predicted.
The newly published Science papers bear that out; click here for a list of top results.
“Observing Pluto and Charon up close has caused us to completely reassess thinking on what sort of geological activity can be sustained on isolated planetary bodies in this distant region of the solar system, worlds that formerly had been thought to be relics little changed since the Kuiper Belt’s formation,” said Jeff Moore, lead author of the geology paper from NASA’s Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California.
Scientists studying Pluto’s composition say the diversity of its landscape stems from eons of interaction between highly volatile and mobile methane, nitrogen and carbon monoxide ices with inert and sturdy water ice. “We see variations in the distribution of Pluto’s volatile ices that point to fascinating cycles of evaporation and condensation,” said Will Grundy of the Lowell Observatory, Flagstaff, Arizona, lead author of the composition paper. “These cycles are a lot richer than those on Earth, where there’s really only one material that condenses and evaporates – water. On Pluto, there are at least three materials, and while they interact in ways we don’t yet fully understand, we definitely see their effects all across Pluto’s surface.”
This enhanced color view of Pluto’s surface diversity was created by merging Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) color imagery (650 meters or 2,132 feet per pixel) with Long Range Reconnaissance Imager panchromatic imagery (230 meters or 755 feet per pixel). At lower right, ancient, heavily cratered terrain is coated with dark, reddish tholins. At upper right, volatile ices filling the informally named Sputnik Planum have modified the surface, creating a chaos-like array of blocky mountains. Volatile ice also occupies a few nearby deep craters, and in some areas the volatile ice is pocked with arrays of small sublimation pits. At left, and across the bottom of the scene, gray-white methane ice deposits modify tectonic ridges, the rims of craters, and north-facing slopes. The scene in this image is 260 miles (420 kilometers) wide and 140 miles (225 kilometers) from top to bottom; north is to the upper left. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI
Above the surface, scientists discovered Pluto’s atmosphere contains layered hazes, and is both cooler and more compact than expected. This affects how Pluto’s upper atmosphere is lost to space, and how it interacts with the stream of charged particles from the sun known as the solar wind. “We’ve discovered that pre-New Horizons estimates wildly overestimated the loss of material from Pluto’s atmosphere,” said Fran Bagenal, from the University of Colorado, Boulder, and lead author of the particles and plasma paper. “The thought was that Pluto’s atmosphere was escaping like a comet, but it is actually escaping at a rate much more like Earth’s atmosphere.”
SwRI’s Randy Gladstone of San Antonio is the lead author of the Science paper on atmospheric findings. He added, “We’ve also discovered that methane, rather than nitrogen, is Pluto’s primary escaping gas. This is pretty surprising, since near Pluto’s surface the atmosphere is more than 99 percent nitrogen.”
Scientists also are analyzing the first close-up images of Pluto’s small moons—Styx, Nix, Kerberos and Hydra. Discovered between 2005 and 2012, the four moons range in diameter from about 25 miles (40 kilometers) for Nix and Hydra to about six miles (10 kilometers) for Styx and Kerberos. Mission scientists further observed that the small satellites have highly anomalous rotation rates and uniformly unusual pole orientations, as well as icy surfaces with brightness and colors distinctly different from those of Pluto and Charon.
They’ve found evidence that some of the moons resulted from mergers of even smaller bodies, and that their surface ages date back at least 4 billion years. “These latter two results reinforce the hypothesis that the small moons formed in the aftermath of a collision that produced the Pluto-Charon binary system,” said Hal Weaver, New Horizons project scientist from the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, and lead author of the Science paper on Pluto’s small moons.
About half of New Horizons’ flyby data has now been transmitted home – from distances where radio signals at light speed need nearly five hours to reach Earth – with all of it expected back by the end of 2016.
“This is why we explore,” said Curt Niebur, New Horizons program scientist at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “The many discoveries from New Horizons represent the best of humankind and inspire us to continue the journey of exploration to the solar system and beyond.”
Source: NASA